Data analytics, AI and ML (machine learning), and other techniques are proving to better predict vendor behavior and assist with management processes.
Vendor Management
Now is the moment to delve into the crucial role of vendor management, examining its myriad advantages, significant hurdles, and strategies for enhancing vendor partnerships to propel business triumph.
Stay competitive and up to speed by mastering common roadblocks within vendor management. We’ll help you along.
Mastering vendor reconciliation requires precision in adhering to foundational best practices and implementing advanced strategies, as businesses strive for financial excellence and operational resilience.
Highlighting the crucial role of vendor reconciliation guarantees business transparency, averts financial pitfalls, and optimizes cash flow, informed budgeting, and resilient supply chains.
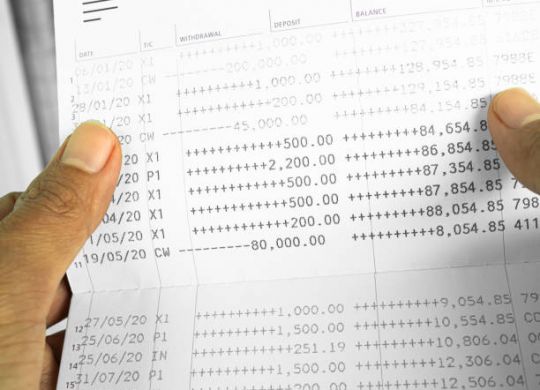
Cross-referencing information, accuracy with payment dates and credit notes, and meticulously maintained records are essential for accurate vendor statements. Read on.
Unlock efficient vendor reconciliation with our guide—blending basics and advanced strategies for precise financial practices and enduring success.
Leverage the latest advancements in AI, ensuring your financial operations are future-proof!
Continue the journey toward efficient financial record keeping by delving into more advanced strategies within Vendor Statement Reconciliation.
Efficient corporate management is crucial to ensure that your organization turns over profit year on year. A good vendor relationship will help you save tremendously in expenses because you won’t have to maintain an in-house software development team. Explore vendor relationship management, what it is and why it matters.